Search¶
Challenge 1 Tri City Search¶
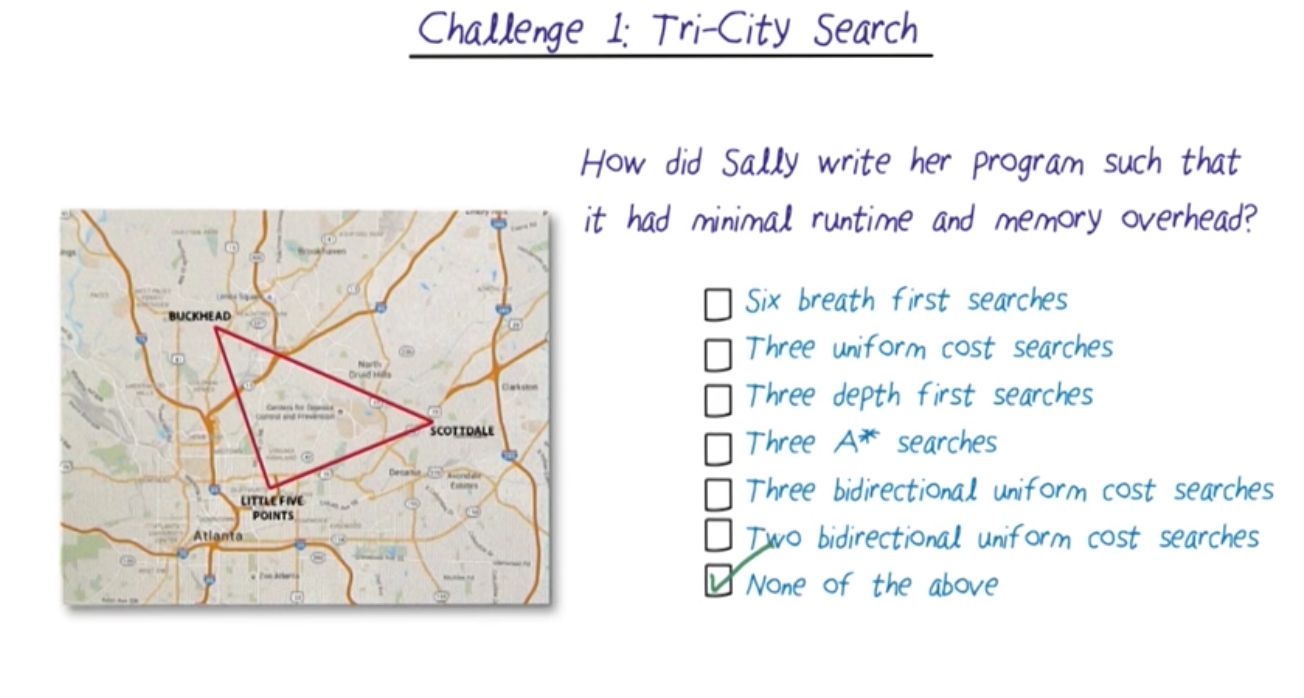
Tri-directional A* search
Challenge 2 Rubik’s Cube¶


Problem Solving¶

Complexity from the many choices.

Complexity comes from partial observability.
Question: Can we find the direction from Arad to Bucharest from this map?

What is a problem¶
Agent is given a problem of coming up with a sequence of actions to find a path from Arad to Bucharest.

Definition of the problem
Initial State
Actions(s) -> {a1, a2, a3 }
Result(s, a) -> s’
GoalTest(s) -> T|F
Path Cost

Example Route Finding¶

Tree Search¶

Breadth-First Search

Tree Search Continued¶



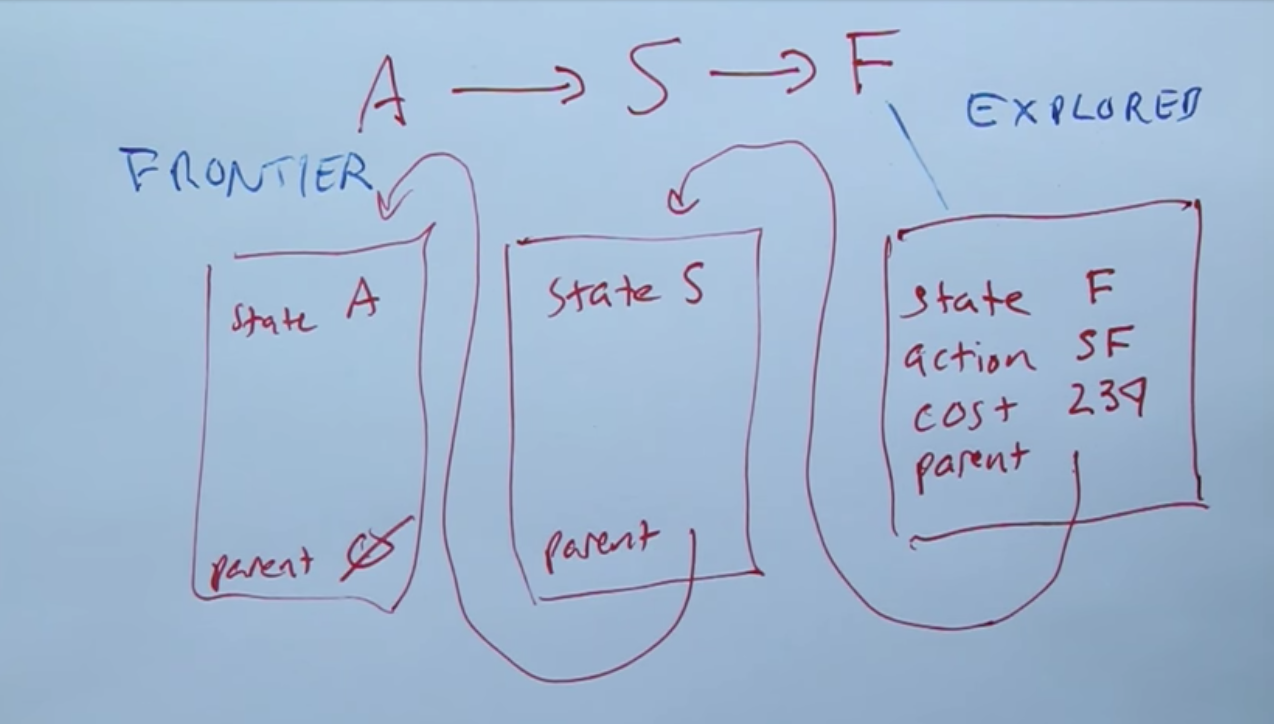
In the preliminary algorithm, A is repeated since we are not keeping track of explored states. Ideally, we would not add duplicates from backtracking.
Graph Search¶

Breadth First Search-1¶
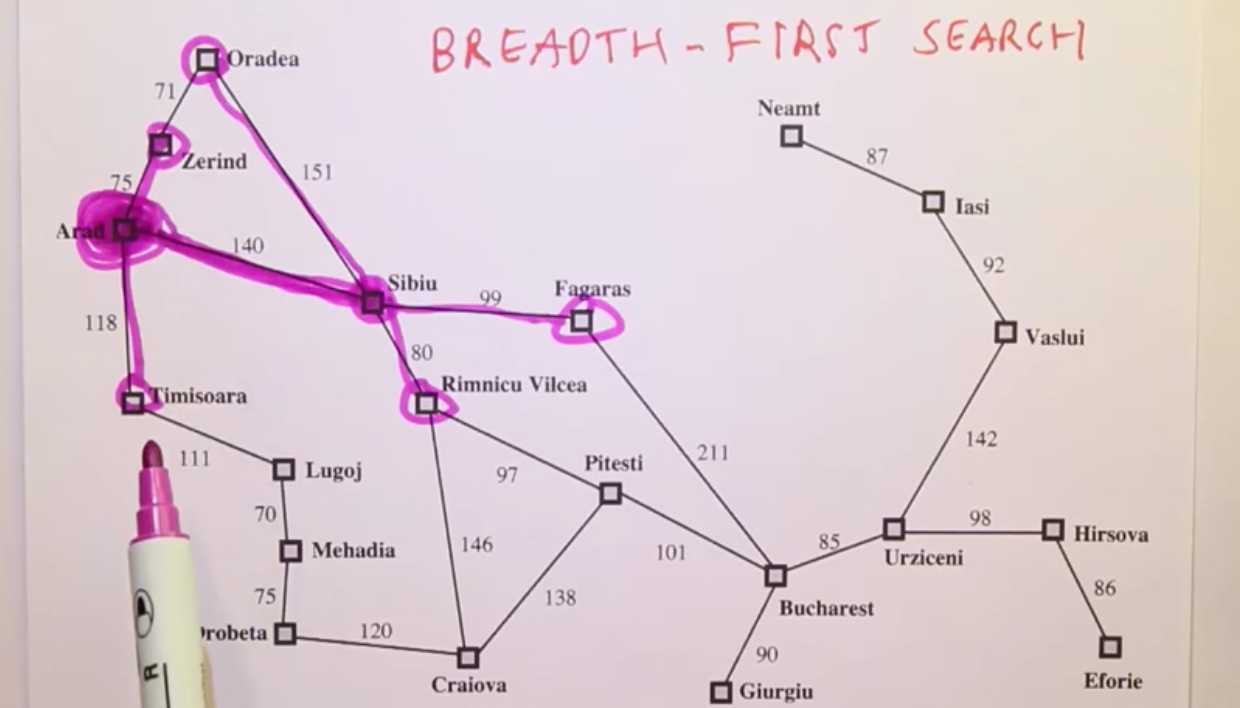
Breadth First Search 3¶

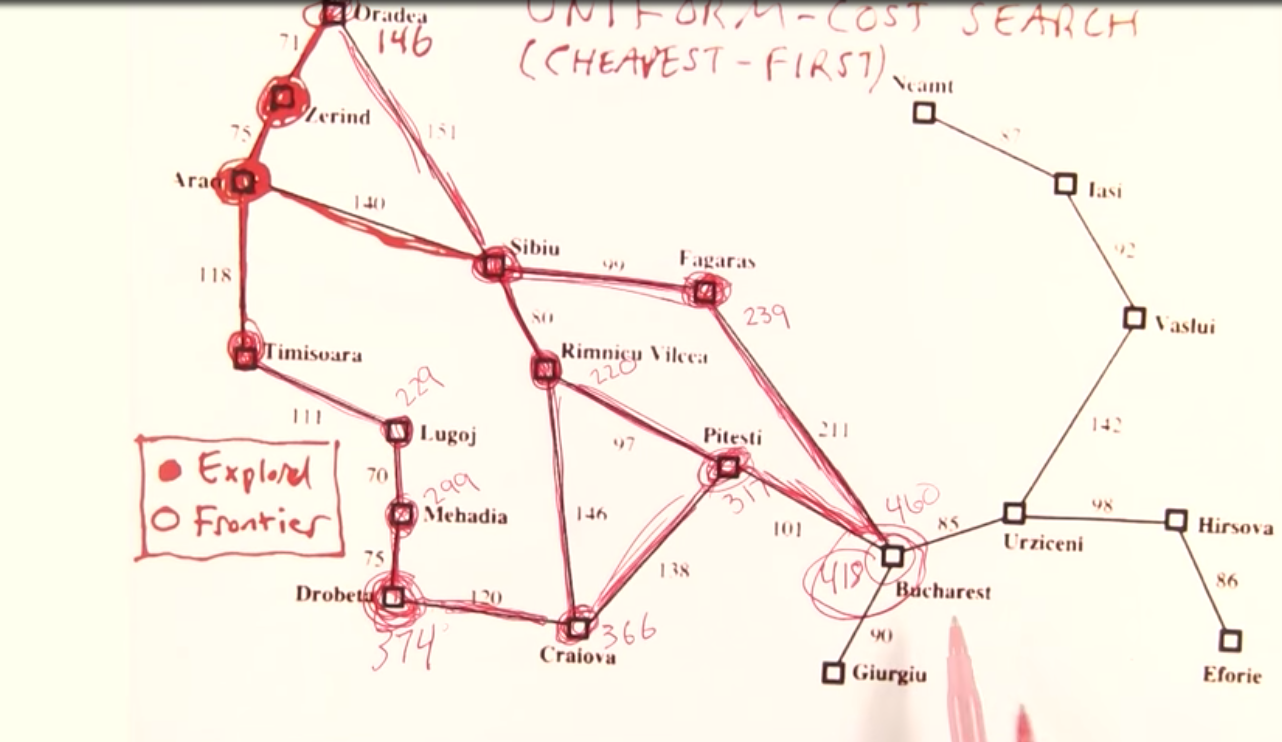
Uniform Cost Search¶
Cheapest path cost search.





Search Comparison¶


Search Comparison - 1¶

Search Comparison 2¶

Are these algorithms complete?

More On Uniform Cost¶

Greedy Best-First Search


A* = Greedy Best First Search + Uniform Cost Search
A* Search¶





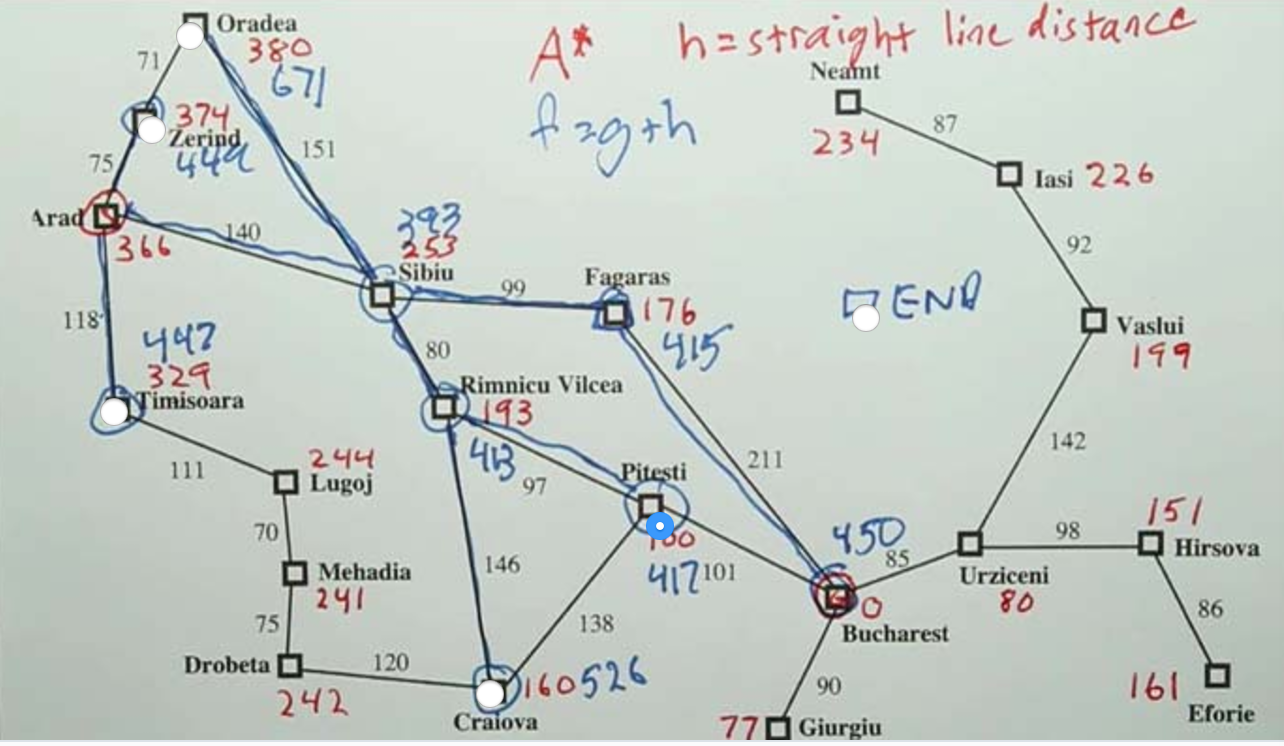


Admissible Heuristic Function¶
Heuristic function is admissible if h(s) <= true cost, rather than necessarily being strictly smaller than the true cost.
h should never overestimate the distance to the goal.
h should be optimistic
h is admissible.
Optimistic Heuristic¶

State Spaces¶


Robot can be A or B = 2
World itself
State A can be dirty or not = 2
State B can be dirty or not = 2
Total = 2 x 2 x 2 = 8 state spaces.
State Spaces 2¶


Sliding Blocks Puzzle¶

Sliding Blocks Puzzle 2¶

Generating a relaxed problem.
Problems With Search¶

A Note On Implementation¶
References¶
Korf, 1997, Finding Optimal Solutions to Rubik’s Cube Using Pattern Databases.
Goldberg, 2011. Reach for A* An Efficient Point-to-Point Shortest Path Algorithm
Goldberg & Harrelson, March 2003. Computing the Shortest Path A* Search Meets Graph Theory.
Gutman, 2004. Reach-based Routing A New Approach to Shortest Path Algorithms Optimized for Road Networks.